RNA and protein synthesis problem set delves into the intricate mechanisms that govern the synthesis of proteins, the fundamental building blocks of life. This problem set explores the processes of transcription and translation, unraveling the complex relationship between RNA and protein synthesis.
By understanding these processes, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of cellular machinery and its profound impact on various biological functions.
The problem set encompasses a thorough examination of transcription, including the role of RNA polymerase and DNA in the production of different RNA molecules. It delves into the intricacies of translation, shedding light on the roles of ribosomes, tRNA, and mRNA in the intricate dance of protein synthesis.
Furthermore, the problem set investigates the various levels of protein structure, from primary to quaternary, and explores the relationship between protein structure and function.
Introduction: Rna And Protein Synthesis Problem Set
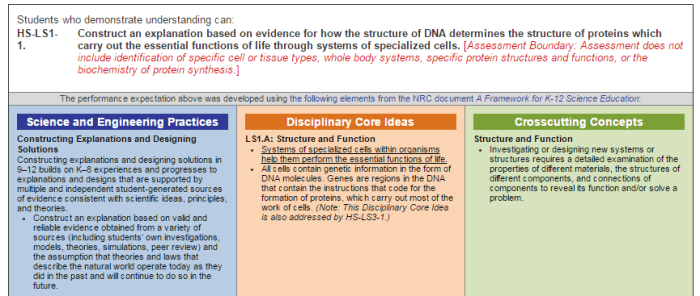
RNA and protein synthesis are fundamental processes in molecular biology that allow cells to create and maintain their complex structures and functions. Understanding the relationship between RNA and protein synthesis is crucial for comprehending the inner workings of cells and their role in health and disease.
Transcription
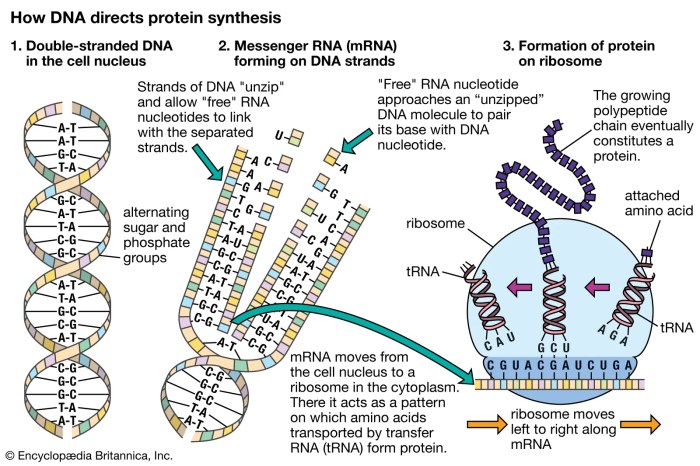
Transcription is the first step in gene expression, where the genetic information encoded in DNA is copied into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This process is carried out by RNA polymerase, an enzyme that binds to the DNA template and synthesizes a complementary mRNA strand.
Types of RNA Molecules
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): Carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- Transfer RNA (tRNA): Transfers specific amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): Forms the structural components of ribosomes, the cellular machinery for protein synthesis.
Regulation of Transcription
- Promoter regions: DNA sequences that bind RNA polymerase and initiate transcription.
- Enhancers: DNA sequences that enhance the binding of RNA polymerase to promoters.
- Silencers: DNA sequences that suppress the binding of RNA polymerase to promoters.
Translation
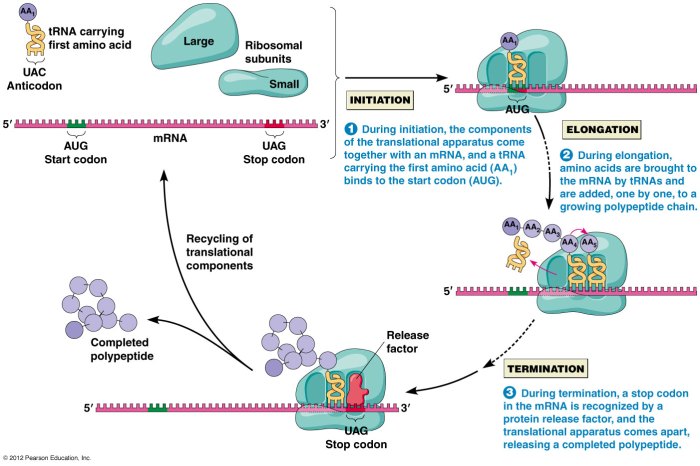
Translation is the second step in gene expression, where the mRNA molecule is decoded to produce a specific protein. This process occurs on ribosomes, which are composed of rRNA and proteins. tRNA molecules carry specific amino acids to the ribosomes, where they are added to the growing polypeptide chain.
Steps of Translation
- Initiation: mRNA binds to the ribosome, and the start codon is recognized.
- Elongation: tRNA molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome, which are added to the growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination: A stop codon is reached, and the polypeptide chain is released.
Regulation of Translation, Rna and protein synthesis problem set
- Ribosomal proteins: Regulate the binding of mRNA and tRNA to the ribosomes.
- Translation factors: Assist in the initiation, elongation, and termination of translation.
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs): Small RNA molecules that can bind to mRNA and inhibit translation.
Query Resolution
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the synthesis of RNA molecules using DNA as a template.
What are the different types of RNA molecules produced during transcription?
The three main types of RNA molecules produced during transcription are messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA (rRNA), and transfer RNA (tRNA).
How is translation regulated?
Translation is regulated at multiple levels, including the availability of ribosomes, tRNA molecules, and regulatory proteins.