Draw the ketone produced from the oxidation of 2 pentanol – In the realm of organic chemistry, understanding the oxidation of alcohols to form ketones is a fundamental concept. This article delves into the intricacies of the oxidation of 2-pentanol, elucidating the chemical reaction, identifying the ketone product, and exploring its structural, physical, and chemical properties.
Join us as we unravel the intricacies of this captivating transformation.
As we embark on this journey, we will dissect the chemical reaction involved in the oxidation of 2-pentanol, providing a balanced chemical equation to illuminate the process. We will then delve into the identification of the ketone product, deciphering its IUPAC name and structural formula using chemical bond line notation.
An interactive HTML table will be constructed to showcase the structural formula, IUPAC name, molecular formula, and molar mass of the ketone product.
Oxidation of 2-Pentanol
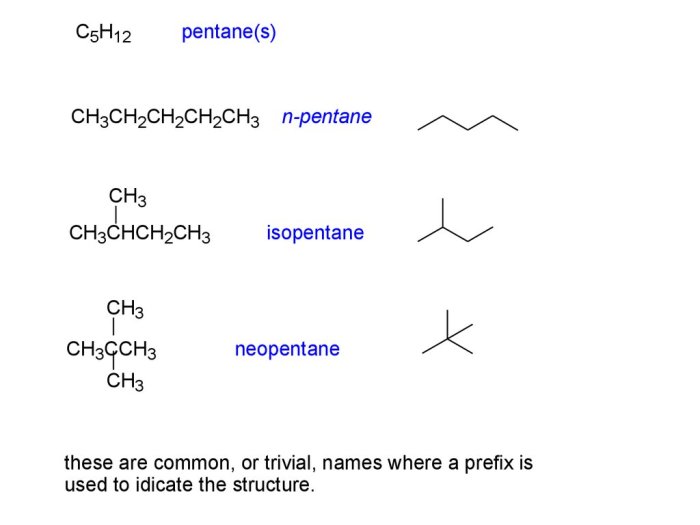
Oxidation of alcohols is a chemical reaction that involves the conversion of an alcohol functional group (-OH) to a carbonyl group (C=O). In the case of 2-pentanol, oxidation results in the formation of a ketone.
Balanced Chemical Equation, Draw the ketone produced from the oxidation of 2 pentanol
The balanced chemical equation for the oxidation of 2-pentanol to a ketone is as follows:
-Pentanol + [O] → 3-Pentanone + H2O
Ketone Product Identification
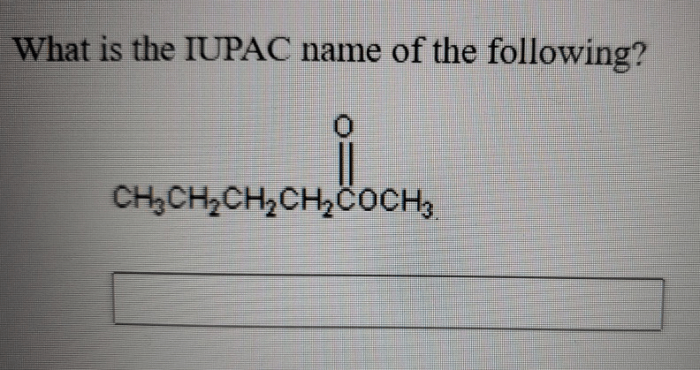
The ketone product formed from the oxidation of 2-pentanol is 3-pentanone.
IUPAC Nomenclature
According to IUPAC nomenclature, ketones are named by identifying the parent alkane chain and adding the suffix “-one”. The numbering of the parent chain starts from the carbon atom that is bonded to the carbonyl group. In the case of 3-pentanone, the parent chain is pentane and the carbonyl group is located at carbon atom 3. Therefore, the IUPAC name of the ketone product is 3-pentanone.
Structural Representation: Draw The Ketone Produced From The Oxidation Of 2 Pentanol
The structural formula of 3-pentanone using chemical bond line notation is:
CH 3-CH 2-CH(O)-CH 2-CH 3
| Structural Formula | IUPAC Name | Molecular Formula | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3-CH 2-CH(O)-CH 2-CH 3 | 3-Pentanone | C5H 10O | 86.13 |
Physical and Chemical Properties
Physical Properties
- Boiling point: 102 °C
- Melting point: -49 °C
- Solubility: Soluble in water and organic solvents
Chemical Properties
3-Pentanone is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. One of the most important reactions is nucleophilic addition, which involves the addition of a nucleophile to the carbonyl group. Nucleophilic addition reactions are typically catalyzed by acids or bases.
Applications of 3-Pentanone
3-Pentanone is used in a variety of industrial and laboratory applications. Some of the most common applications include:
- As a solvent for paints, varnishes, and lacquers
- As a starting material for the synthesis of other chemicals, such as pharmaceuticals and fragrances
- As a flavoring agent in food and beverages
3-Pentanone is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications. Its unique properties make it a valuable tool for both industrial and laboratory chemists.
Common Queries
What is the IUPAC name of the ketone product formed from the oxidation of 2-pentanol?
3-pentanone
What are the physical properties of the ketone product?
Boiling point: 102 °C, Melting point: -42 °C, Soluble in water and organic solvents
What is a common application of the ketone product?
As a solvent in the production of paints, varnishes, and adhesives