Embark on a cartographic adventure with the Reading Topographic Maps Gizmo Answer Key, your indispensable guide to deciphering the intricate language of topographic maps. This key unlocks the secrets of terrain, empowering you to navigate the complexities of the Earth’s surface with confidence and precision.
Delve into the fascinating world of contour lines, map symbols, and cross-sections, gaining a comprehensive understanding of elevation, slope, and aspect. Discover the practical applications of topographic maps in fields such as geology, engineering, and land use planning.
Topographic Maps: Understanding the Basics
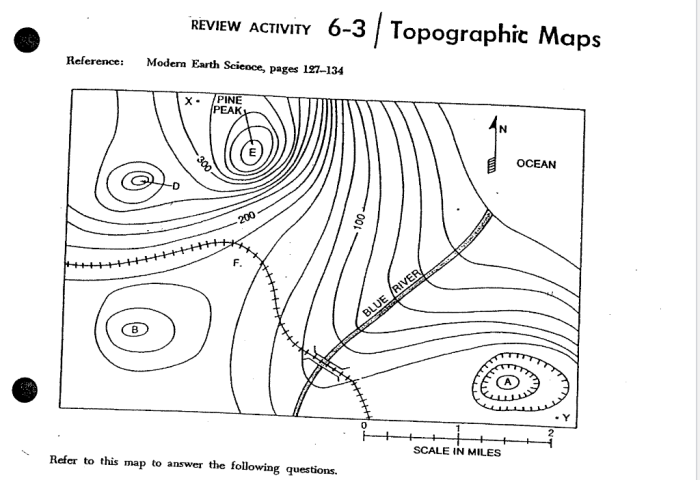
Topographic maps are graphical representations of the Earth’s surface that depict natural and man-made features, along with their elevation and other relevant information. They provide a comprehensive overview of the landscape, enabling users to understand the terrain, plan routes, and make informed decisions.
Types of Topographic Maps
- Topographic Quadrangles: Detailed maps covering a specific geographic area, typically with a scale of 1:24,000 or 1:25,000.
- Planimetric Maps: Similar to topographic quadrangles but lack contour lines, focusing on planimetric features such as roads, buildings, and water bodies.
- Digital Elevation Models (DEMs): Digital representations of the Earth’s surface, providing elevation data in a grid format.
Key Features of Topographic Maps
- Contour Lines: Lines connecting points of equal elevation, representing the shape and slope of the terrain.
- Elevation: The height of a point above a reference datum, typically mean sea level.
- Scale: The ratio between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground.
Contour Lines: A Guide to Reading Elevation

Contour lines are the most prominent feature of topographic maps. They connect points of equal elevation, forming closed loops around hills and valleys. The spacing between contour lines indicates the steepness of the slope: closely spaced lines represent steep slopes, while widely spaced lines indicate gentle slopes.
Determining Slope and Direction
The slope of a contour line can be determined by the spacing between the lines. Steeper slopes have more closely spaced lines, while gentler slopes have more widely spaced lines. The direction of a slope can be determined by the direction of the contour lines: lines that point uphill indicate the direction of steepest ascent.
Map Symbols and Features: Interpreting the Landscape
Topographic maps use a variety of symbols to represent natural and man-made features on the landscape. These symbols are standardized and consistent across maps, allowing users to easily identify and interpret the features they encounter.
Common Map Symbols
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Road | |
| Water Body | |
| Forest |
Interpreting Features
By identifying the symbols and understanding their meanings, users can gain a comprehensive understanding of the landscape depicted on the topographic map. This information can be used for a variety of purposes, such as planning hiking trails, identifying potential building sites, or understanding the flow of water in a watershed.
Distance and Area Measurements: Scaling the Map
Topographic maps include a scale that allows users to measure distances and areas on the map. The scale is typically expressed as a ratio, such as 1:24,000, which means that one unit on the map represents 24,000 units on the ground.
Measuring Distances
To measure distances on a topographic map, use a ruler or measuring tape to determine the distance between two points on the map. Then, multiply this distance by the scale to get the corresponding distance on the ground.
Calculating Areas
To calculate the area of a region on a topographic map, use a grid or planimeter to determine the area on the map. Then, multiply this area by the scale squared to get the corresponding area on the ground.
Cross-Sections: Visualizing the Terrain
Cross-sections are vertical profiles of the landscape that provide a detailed view of the elevation and slope of the terrain along a specific line. They are constructed by drawing a line on the topographic map and plotting the elevation of the terrain along that line.
Creating Cross-Sections, Reading topographic maps gizmo answer key
To create a cross-section, draw a line on the topographic map along the desired path. Then, measure the elevation of the terrain at regular intervals along the line. Plot these elevations on a graph, with the horizontal axis representing distance and the vertical axis representing elevation.
Significance of Cross-Sections
Cross-sections provide a valuable tool for understanding the three-dimensional structure of the terrain. They can be used to identify valleys, ridges, and other landforms, as well as to analyze the slope and aspect of the terrain.
Slope and Aspect: Analyzing the Terrain
Slope is the angle of inclination of the terrain, while aspect is the direction of the slope. Both slope and aspect are important factors in understanding the geomorphology and land use of an area.
Calculating Slope and Aspect
Slope can be calculated using contour lines. The steeper the slope, the closer together the contour lines will be. Aspect can be determined by drawing a line perpendicular to the contour lines at a given point. The direction of this line will indicate the aspect of the slope.
Significance of Slope and Aspect
Slope and aspect influence a variety of factors, including soil erosion, water flow, and vegetation distribution. Understanding slope and aspect is essential for land use planning, environmental management, and other applications.
FAQ Overview: Reading Topographic Maps Gizmo Answer Key
What is the purpose of a topographic map?
Topographic maps provide a detailed representation of the Earth’s surface, including elevation, slope, and natural and man-made features, enabling users to visualize and analyze terrain.
How do contour lines indicate elevation?
Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, forming a series of concentric lines that depict the shape and slope of the land.
What is the significance of cross-sections in topographic map analysis?
Cross-sections provide a vertical profile of the terrain, allowing users to visualize the three-dimensional structure of the landscape and understand the relationships between different elevations.