Segmented worms the earthworm answer key – Introducing the segmented worms: the earthworm answer key, this comprehensive guide delves into the intriguing world of earthworms, exploring the significance of their segmented body structure. From aiding in movement to supporting complex biological processes, segmentation plays a crucial role in the survival and adaptation of these fascinating creatures.
Delve into the intricacies of earthworm anatomy, uncovering the specialized functions of each segment. Witness the remarkable digestive system, understanding how segmentation facilitates efficient nutrient absorption. Discover the mechanisms behind earthworm movement, unraveling the contribution of body segmentation to their unique locomotion.
Earthworm Body Segmentation

Earthworms exhibit a distinct body segmentation, a remarkable adaptation that provides numerous benefits and aids in their survival and functionality.
The body of an earthworm is divided into numerous segments, each serving specific functions and contributing to the overall efficiency of the organism.
Different Types of Body Segments in an Earthworm
Earthworms typically possess three main types of body segments:
- Preclitellar segments:Located at the anterior end, these segments house the mouth, pharynx, and other sensory organs.
- Clitellum:A thickened, saddle-shaped segment found near the middle of the body, responsible for reproduction.
- Postclitellar segments:The remaining segments behind the clitellum, housing the digestive, circulatory, and excretory systems.
Body Segmentation and Earthworm Movement, Segmented worms the earthworm answer key
Body segmentation plays a crucial role in earthworm movement. The muscles within each segment contract and relax, allowing the worm to elongate and shorten its body.
Additionally, the fluid-filled coelom between segments provides hydrostatic support, enabling the worm to move through the soil and navigate its environment.
Earthworm Anatomy and Segmentation
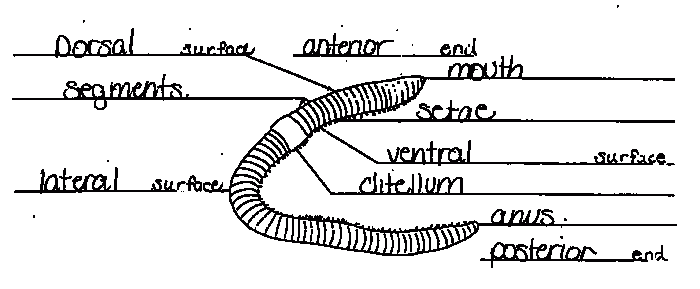
| Segment | Location | Function | Special Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prostomium | Anterior end | Sensing and feeding | Contains mouth and sensory organs |
| Peristomium | First body segment | Contains mouth and pharynx | – |
| Clitellum | Middle segments | Reproduction | Thickened, saddle-shaped |
| Setae | All segments except clitellum | Movement and anchoring | Small, hair-like projections |
| Nephridia | All segments except clitellum | Excretion | Small, coiled tubules |
| Typhlosole | Postclitellar segments | Nutrient absorption | Internal fold in the digestive tract |
Earthworm Digestive System and Segmentation
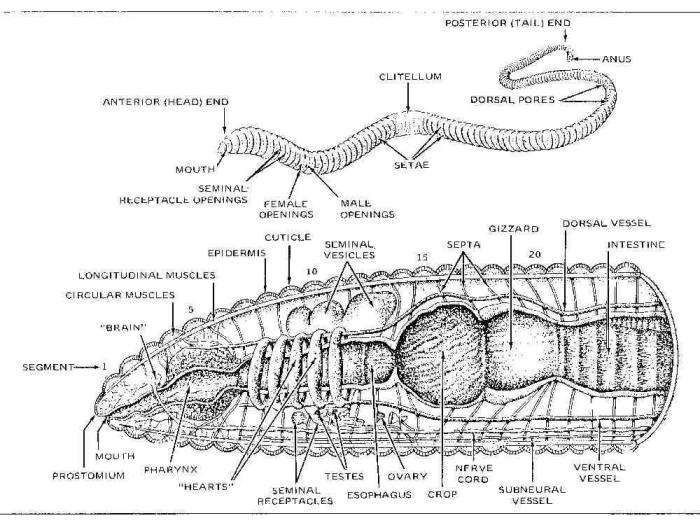
The segmentation of an earthworm’s body supports its digestive system in several ways:
- Pharynx:Located in the first segment, the pharynx sucks in organic matter.
- Esophagus:Connects the pharynx to the crop, where food is stored.
- Gizzard:Grinds down ingested food, aided by small stones swallowed by the worm.
- Intestine:Where most digestion and nutrient absorption occur, aided by the typhlosole.
- Anus:Located in the last segment, where undigested material is expelled.
Each segment contributes to the efficient movement of food through the digestive tract.
Earthworm Movement and Segmentation: Segmented Worms The Earthworm Answer Key
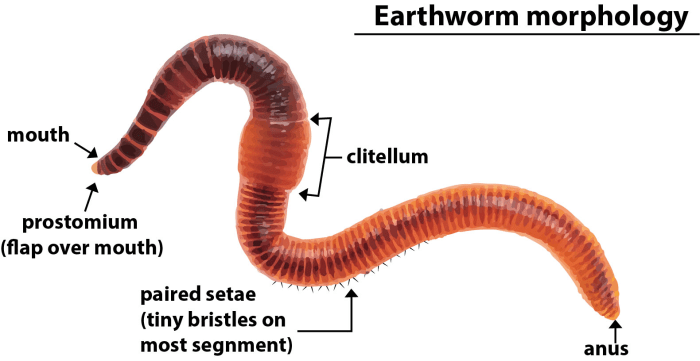
Earthworms move primarily through peristalsis, a wave-like contraction of muscles along their body.
Segmentation facilitates this movement by allowing different segments to contract and relax independently.
Earthworms use their segmented bodies to navigate various environments, including:
- Burrowing:Using their pointed anterior end and muscular contractions to penetrate the soil.
- Crawling:Moving across the surface by extending and contracting their body.
- Swimming:Some earthworm species can swim in water by undulating their bodies.
Earthworm Reproduction and Segmentation
Body segmentation plays a crucial role in earthworm reproduction.
Earthworms are hermaphroditic, meaning they possess both male and female reproductive organs.
The clitellum, a thickened segment near the middle of the body, produces a cocoon that houses developing embryos.
During mating, two earthworms exchange sperm, which is stored in special sacs called spermathecae.
The eggs and sperm are released into the cocoon, where fertilization and development occur.
Earthworm Regeneration and Segmentation
Earthworms possess a remarkable ability to regenerate lost body parts.
If a worm loses a portion of its body, the remaining segments can regenerate the missing tissue.
The regenerative process involves the proliferation of new cells and the reorganization of existing tissues.
Segmentation allows for the isolation of damaged segments, preventing the spread of damage to other parts of the body.
Clarifying Questions
What is the primary function of body segmentation in earthworms?
Body segmentation in earthworms provides structural support, facilitates movement, and compartmentalizes various organs and tissues for efficient functioning.
How does segmentation contribute to earthworm movement?
Segmentation allows earthworms to contract and expand different body segments, generating a wave-like motion that propels them forward or backward.
What is the role of segmentation in earthworm digestion?
The digestive tract of earthworms is divided into specialized segments, each performing specific functions such as food storage, grinding, and nutrient absorption.